5G vs 6G technology represents the next evolution in wireless connectivity. Consequently, understanding these differences helps businesses and consumers prepare for the future. Furthermore, while 5G networks continue expanding globally, 6G research accelerates toward commercial deployment by 2030.
This comprehensive guide explores both technologies in depth. Specifically, we’ll examine speed capabilities, latency improvements, and practical applications. In addition, you’ll discover which technology matters for your needs today.
What Is 5G Technology?
5G represents the fifth generation of wireless network technology. Moreover, it delivers significantly faster speeds than its 4G predecessor. Typically, 5G networks achieve download speeds between 100 Mbps and 10 Gbps.
Key Features of 5G Networks
5G technology operates on three distinct spectrum bands. Consequently, each band offers unique advantages for different applications. The low-band spectrum provides broad coverage, while high-band millimeter waves deliver exceptional speeds.
- Download speeds up to 10 Gbps in optimal conditions
- Ultra-low latency around 1-4 milliseconds
- Enhanced capacity supporting 1 million devices per square kilometer
- Improved energy efficiency compared to 4G networks
- Network slicing for customized connectivity solutions
Furthermore, 5G enables transformative technologies like autonomous vehicles. In addition, it powers smart cities, remote surgery, and industrial automation. GSMA reports confirm these applications require the reliability and speed that 5G provides.
Understanding 6G: The Future of Connectivity
6G technology represents the next wireless frontier after 5G. Specifically, researchers expect commercial deployment around 2030. Meanwhile, early trials and standardization efforts continue worldwide.
Theoretical Capabilities of 6G
6G promises revolutionary improvements over current networks. Consequently, theoretical speeds could reach 1 terabit per second. Additionally, latency may drop below 1 millisecond consistently.
- Peak data rates exceeding 1 Tbps (1000 Gbps)
- Sub-millisecond latency for instantaneous communication
- Integration with AI for intelligent network management
- Terahertz frequency bands for unprecedented bandwidth
- Holographic communication and immersive experiences
Moreover, 6G aims to seamlessly connect physical and digital worlds. In addition, it will enable brain-computer interfaces and advanced AI applications. According to ITU’s research on future networks, these capabilities remain largely theoretical at present.
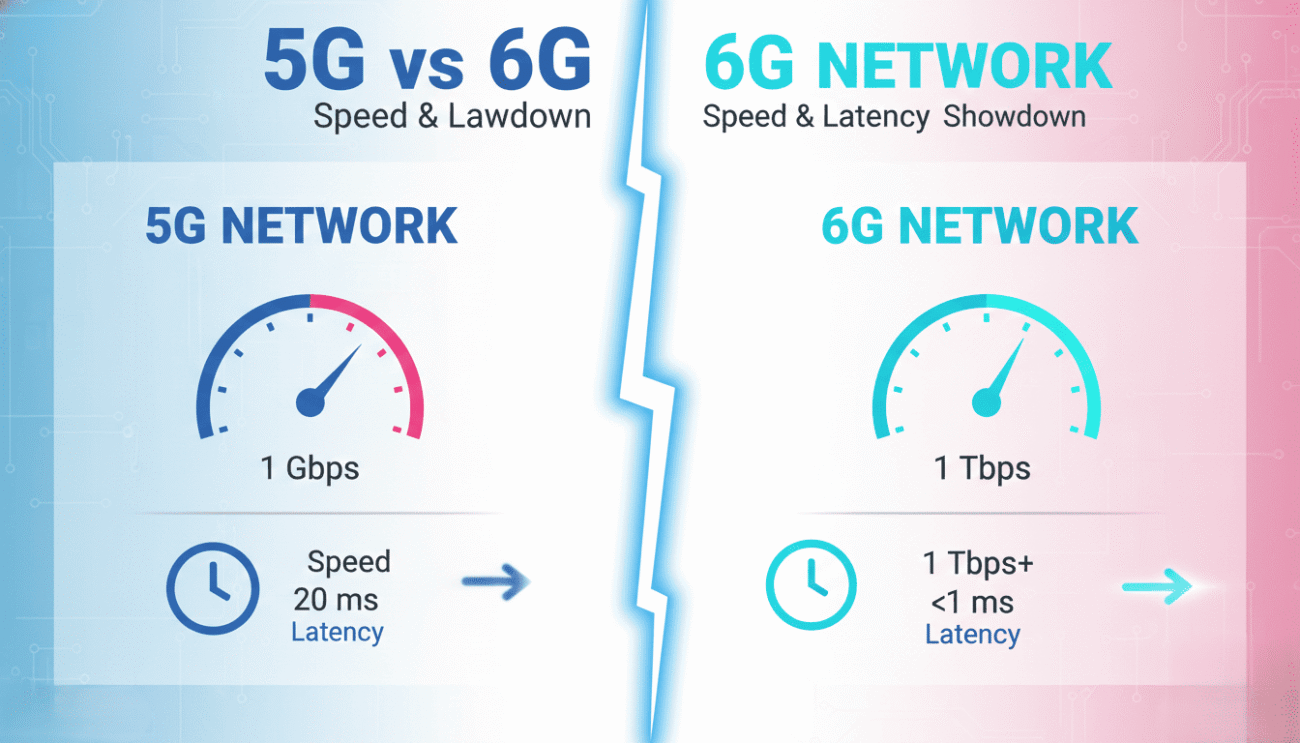
5G vs 6G: Speed and Performance Comparison
Speed differences between 5G and 6G are substantial. Specifically, 6G could deliver 100 times faster speeds than 5G. However, real-world performance depends on infrastructure and deployment.
Download Speed Analysis
5G networks currently achieve practical speeds around 200-400 Mbps. Consequently, users experience excellent performance for streaming and gaming. According to Ookla’s Speedtest Intelligence, 5G speeds continue improving globally. In contrast, 6G targets speeds exceeding 100 Gbps under optimal conditions.
Furthermore, peak theoretical 5G speeds reach 10-20 Gbps. Meanwhile, 6G aims for 1 Tbps or higher. These improvements enable entirely new application categories.
Latency Improvements
Latency represents the delay between sending and receiving data. Therefore, lower latency creates more responsive experiences. 5G typically achieves 1-4 milliseconds latency, while 6G targets sub-millisecond performance.
Frequency Bands: How 5G vs 6G Differ
Frequency spectrum fundamentally differentiates these technologies. Specifically, 5G utilizes frequencies up to 100 GHz. Conversely, 6G explores terahertz bands between 100 GHz and 10 THz.
5G Spectrum Allocation
5G operates across low, mid, and high-band frequencies. Consequently, carriers balance coverage and speed strategically. Low-band (below 1 GHz) provides wide coverage, while millimeter wave (24-100 GHz) delivers maximum speed.
6G Terahertz Potential
6G will leverage previously unused terahertz frequencies. Furthermore, these bands offer massive bandwidth for data transmission. However, terahertz signals face significant propagation challenges requiring innovative solutions.
Real-World Applications: 5G vs 6G Use Cases
Both technologies enable transformative applications across industries. However, their capabilities suit different needs and timelines. Consequently, understanding practical applications helps assess their value.
Current 5G Applications
5G already powers numerous real-world solutions today. Specifically, enhanced mobile broadband transforms consumer experiences. Additionally, industrial IoT applications optimize manufacturing processes.
- Ultra-HD video streaming and cloud gaming
- Smart city infrastructure and traffic management
- Remote medical consultations and telemedicine
- Industrial automation and predictive maintenance
- Autonomous vehicle communication systems
Future 6G Possibilities
6G will unlock applications currently impossible with existing technology. Moreover, it will deeply integrate AI and machine learning. These capabilities create unprecedented opportunities for innovation.
- Holographic telepresence and immersive communication
- Brain-computer interfaces for direct neural connectivity
- Fully autonomous smart cities with AI coordination
- Real-time language translation with zero latency
- Advanced mixed reality experiences indistinguishable from reality
Infrastructure Requirements: Building 5G vs 6G Networks
Infrastructure needs differ dramatically between these technologies. Consequently, deployment complexity and cost vary significantly. Furthermore, 6G requires entirely new infrastructure approaches.
5G Network Infrastructure
5G deployment requires dense small cell networks. Specifically, millimeter wave signals necessitate frequent cell sites. Additionally, fiber backhaul connections ensure adequate capacity.
Moreover, 5G infrastructure builds upon existing cellular frameworks. Therefore, carriers upgrade incrementally from 4G foundations. This approach accelerates deployment while managing costs.
6G Infrastructure Challenges
6G networks demand revolutionary infrastructure innovations. Specifically, terahertz propagation requires extremely dense deployments. In addition, intelligent reflecting surfaces may redirect signals around obstacles.
Furthermore, satellite integration becomes essential for 6G coverage. Consequently, space-based networks will complement terrestrial infrastructure. These systems work together seamlessly.
Energy Efficiency: Environmental Impact Comparison
Energy consumption critically impacts network sustainability. Therefore, both technologies prioritize efficiency improvements. However, their approaches and results differ substantially.
5G Energy Performance
5G networks demonstrate improved energy efficiency per bit transmitted. Consequently, operators reduce environmental impact while increasing capacity. Advanced sleep modes and intelligent resource allocation optimize power consumption.
6G Sustainability Goals
6G aims for carbon-neutral network operations. Specifically, researchers target 90% energy reduction compared to 5G. IEEE Spectrum research highlights sustainability as a core 6G objective. Additionally, AI-driven optimization minimizes waste throughout the network.
Timeline and Availability: When to Expect 5G vs 6G
Deployment timelines significantly differ between these technologies. Specifically, 5G continues expanding globally today. Conversely, 6G remains in early research phases.
5G Deployment Status
5G networks operate in numerous countries worldwide currently. Moreover, coverage expands rapidly in urban areas. However, rural deployment progresses more gradually due to infrastructure costs.
Furthermore, most major carriers now offer 5G services. Consequently, consumers can access enhanced connectivity in many locations. Device availability also increases continuously.
6G Development Timeline
6G standardization begins around 2025-2026. Subsequently, initial deployments may start around 2030. However, widespread availability likely won’t occur until 2035 or later.
Moreover, research organizations worldwide collaborate on 6G specifications. 3GPP (3rd Generation Partnership Project) coordinates global standardization efforts. In addition, governments invest billions in development programs. These efforts accelerate progress toward commercialization.
Cost Considerations: Investment Required for Each Technology
Financial implications affect both consumers and service providers. Consequently, understanding cost differences helps planning and budgeting. Furthermore, infrastructure investments determine deployment pace.
5G Cost Analysis
5G infrastructure requires substantial capital investment. Specifically, carriers spend billions upgrading networks globally. However, consumer device costs have decreased significantly recently.
Moreover, 5G service plans typically cost slightly more than 4G. Nevertheless, prices continue declining as competition increases. Additionally, the value proposition improves with expanding coverage.
Projected 6G Expenses
6G development and deployment will cost trillions globally. Consequently, international cooperation becomes essential for success. Furthermore, early 6G devices will command premium prices initially.
Device Compatibility: What Works with 5G vs 6G
Device ecosystems differ significantly between network generations. Therefore, consumers must consider compatibility when purchasing equipment. Furthermore, backward compatibility ensures smooth transitions.
5G Device Ecosystem
5G smartphones and devices are widely available today. Moreover, prices range from budget to premium options. Consequently, consumers can choose devices matching their needs and budgets.
Furthermore, most new smartphones include 5G connectivity standard. Additionally, IoT devices increasingly support 5G networks. This broad ecosystem accelerates adoption rates.
Future 6G Devices
6G devices remain in conceptual stages currently. However, they will incorporate advanced AI capabilities natively. Additionally, new form factors may emerge specifically for 6G networks.
Moreover, holographic displays and neural interfaces require specialized hardware. Consequently, 6G devices will differ dramatically from current smartphones. These innovations create exciting possibilities.
Security and Privacy: Comparing 5G vs 6G Protection
Security features critically impact network adoption and trust. Consequently, both technologies prioritize enhanced protection mechanisms. However, their approaches reflect different threat landscapes.
5G Security Features
5G incorporates improved encryption and authentication protocols. Specifically, network slicing enables isolated security domains. Additionally, edge computing reduces data transmission vulnerabilities.
Furthermore, 5G addresses known 4G security weaknesses. Nevertheless, new vulnerabilities continue emerging as technology evolves. Therefore, continuous security updates remain essential.
6G Security Innovations
6G aims for quantum-resistant encryption by default. Moreover, AI-powered threat detection identifies attacks in real-time. Consequently, security becomes proactive rather than reactive.
Additionally, 6G integrates blockchain for decentralized security. Furthermore, zero-trust architectures verify every connection continuously. These approaches significantly enhance protection.
Conclusion: Which Technology Matters for You?
5G vs 6G comparison reveals complementary technologies serving different timelines. Specifically, 5G delivers tangible benefits today for consumers and businesses. Meanwhile, 6G promises revolutionary capabilities arriving next decade.
For immediate needs, 5G provides excellent performance and growing availability. Consequently, upgrading to 5G devices and services makes sense now. Furthermore, 5G infrastructure continues improving rapidly.
However, 6G represents the long-term future of connectivity. Therefore, understanding its potential helps strategic planning. Additionally, early research investments position organizations for future success.
Ultimately, both technologies advance human connectivity significantly. Moreover, they enable innovations transforming society fundamentally. Consequently, staying informed about both ensures optimal technology decisions.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the main difference between 5G and 6G?
The main difference is speed and latency. 5G offers speeds up to 10 Gbps with 1-4ms latency, while 6G targets 1 Tbps speeds with sub-millisecond latency. Additionally, 6G will use terahertz frequencies and integrate AI natively.
When will 6G be available to consumers?
6G commercial deployment is expected around 2030, with widespread availability likely by 2035. Currently, 6G remains in the research phase, with standardization beginning around 2025-2026.
Can my current 5G phone work on 6G networks?
No, 5G devices will not be compatible with 6G networks. 6G requires entirely new hardware supporting terahertz frequencies and advanced capabilities. However, 6G networks will likely support backward compatibility with 5G.
Is 5G fast enough, or should I wait for 6G?
5G is more than adequate for current needs, offering excellent speeds and low latency. Since 6G won’t arrive commercially until 2030 or later, waiting isn’t practical. Upgrade to 5G now and consider 6G when it becomes available.
How much faster will 6G be compared to 5G?
6G could be 100 times faster than 5G theoretically. While 5G peaks at 10-20 Gbps, 6G targets speeds exceeding 1 Tbps (1000 Gbps). However, real-world performance will depend on infrastructure and deployment conditions.